
Breast cancer screening is entering a new era – one where AI is not just assisting but actively transforming how cancer is detected and flagged.
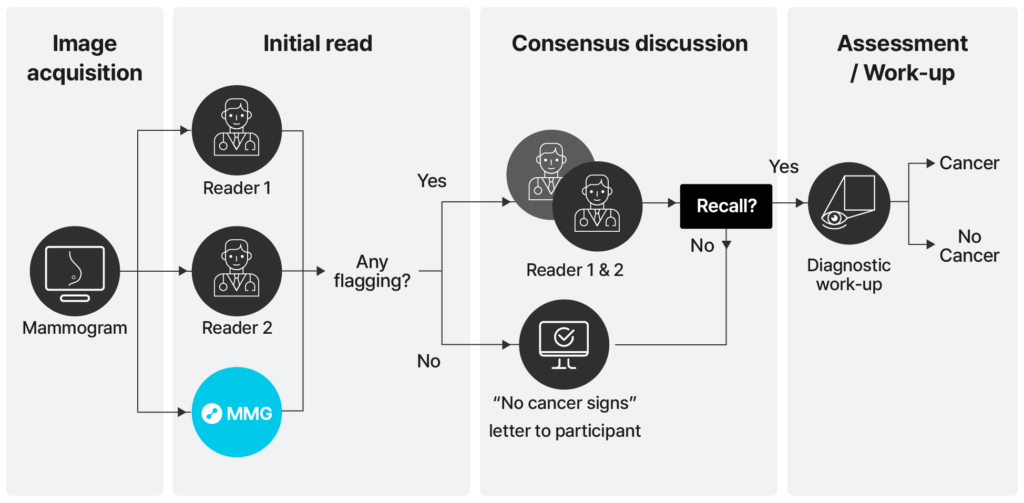
The team at Capio Sverige, in collaboration with Karolinska Institutet, conducted the ScreenTrustCAD study, which explores how radiologists make decisions when using AI in breast cancer screening.
While AI technology is showing impressive results, the study also highlights an important aspect of bringing AI into a predominantly human-led process: trust.

Real-world validation: evidence from over 54,000 cases
By analyzing almost 55,000 cases in women 46-65 years old, the study examined how often cancers were detected when Lunit INSIGHT MMG and radiologists worked in different combinations. The goal was to better understand the trust between radiologists and AI when deciding whether to recall a patient for further testing.
To get a clearer picture of these trust dynamics, the study compared recall rates and Positive Predictive Values (PPV) across cases flagged:
- Only by AI
- Only by a radiologist
- By both AI and a radiologist
- By two radiologists
- By all readers combined.
This approach shed light on how clinical decisions shift depending on who (or what) raises the alarm, revealing important insights into the evolving, but still hesitant, partnership between humans and AI in breast cancer detection.
Building trust: clinical validation in action
Introducing AI into clinical workflows requires more than just technical capability – it demands trust. Radiologists in the study were more likely to recall patients when another radiologist flagged a mammogram, even if the AI had correctly identified something important.
For example, when only a radiologist flagged a mammogram, about 14% of those cases were recalled. However, when only the AI flagged it, only 5% were recalled even though the AI’s picks had much higher PPVs.
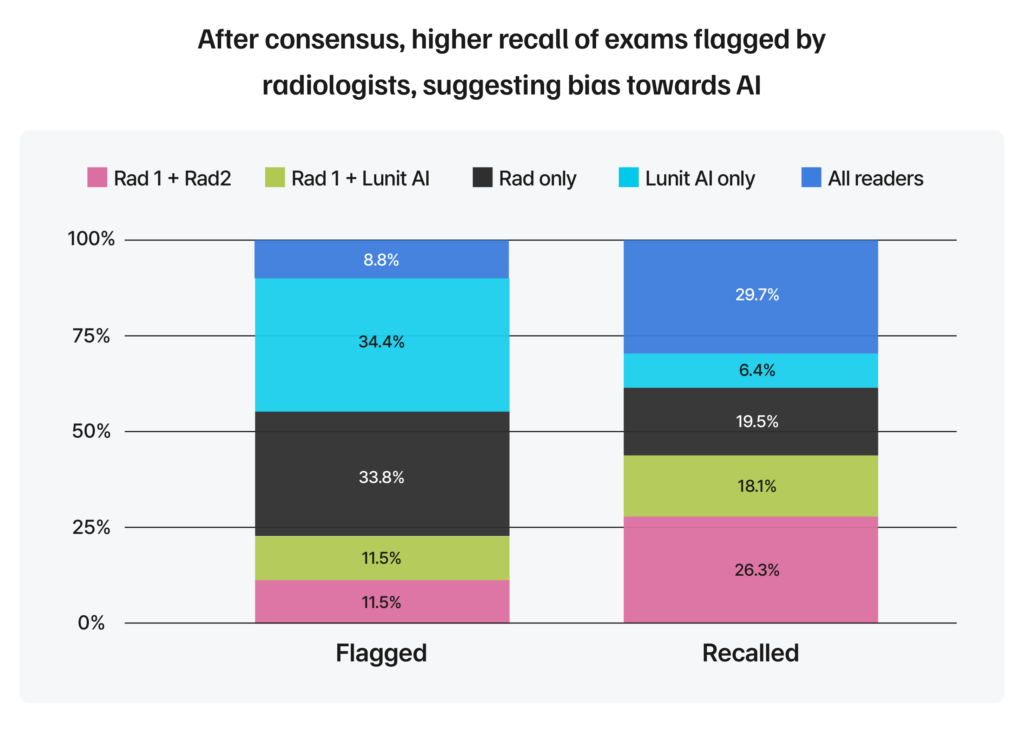
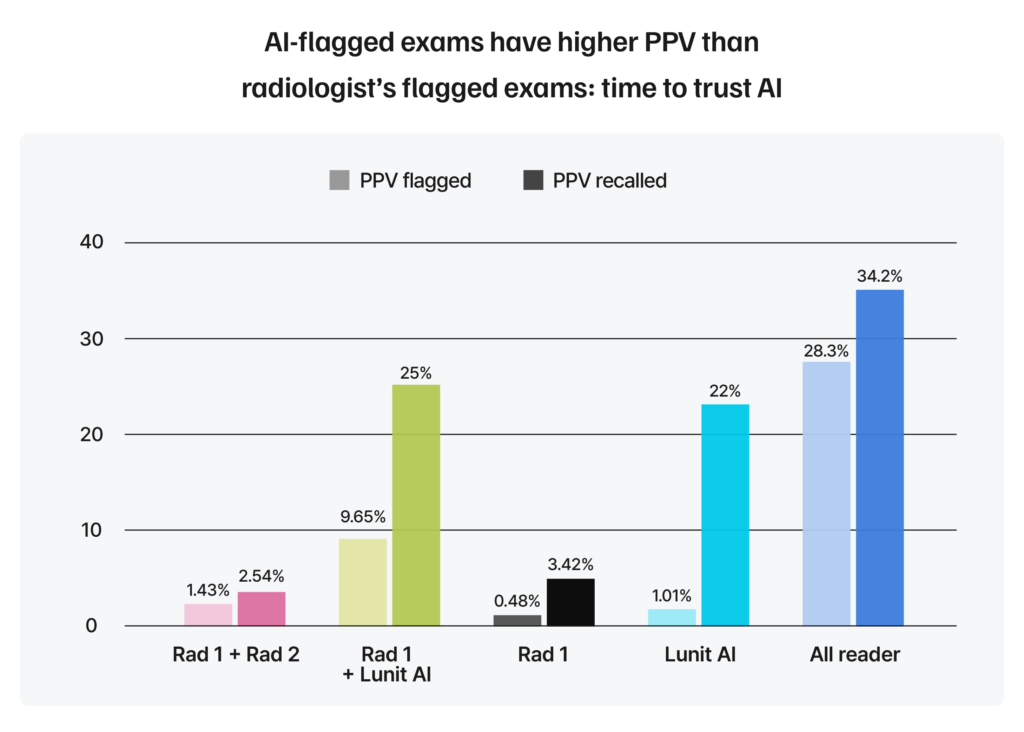
This pattern suggests a bias against acting on AI findings, even when the AI is correct. This human preference can impact how effectively AI is used in real-world screening and highlights the need for building greater trust and understanding between clinicians and AI tools.
The future of screening: collaboration between radiologists and AI is key
This hesitation from radiologists doesn’t diminish the promise of AI, but it does show that building confidence in AI’s role remains a key part of integrating these tools into everyday clinical practices.
AI compliments radiologists’ abilities, helping to improve detection rates, reduce errors, and streamline workflows. As experience grows and collaboration deepens, trust in AI is expected to strengthen, unlocking even greater benefits for patients and care teams alike.
